
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Peking University, College of Future Technology, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Beijing, China
2 Peking University, National Biomedical Imaging Center, Beijing, China
In recent years, notable progress has been achieved in both the hardware and algorithms of structured illumination microscopy (SIM). Nevertheless, the advancement of three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy (3DSIM) has been impeded by challenges arising from the speed and intricacy of polarization modulation. We introduce a high-speed modulation 3DSIM system, leveraging the polarization-maintaining and modulation capabilities of a digital micromirror device (DMD) in conjunction with an electro-optic modulator. The DMD-3DSIM system yields a twofold enhancement in both lateral (133 nm) and axial (300 nm) resolution compared to wide-field imaging and can acquire a data set comprising 29 sections of 1024 pixels × 1024 pixels, with 15 ms exposure time and 6.75 s per volume. The versatility of the DMD-3DSIM approach was exemplified through the imaging of various specimens, including fluorescent beads, nuclear pores, microtubules, actin filaments, and mitochondria within cells, as well as plant and animal tissues. Notably, polarized 3DSIM elucidated the orientation of actin filaments. Furthermore, the implementation of diverse deconvolution algorithms further enhances 3D resolution. The DMD-based 3DSIM system presents a rapid and reliable methodology for investigating biomedical phenomena, boasting capabilities encompassing 3D superresolution, fast temporal resolution, and polarization imaging.
digital micromirror device electro-optic modulation polarization three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(1): 016001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Peking University, College of Future TechnologyDepartment of Biomedical EngineeringBeijing, China
The article presents key principles of an approach to writing impactful review articles.
Advanced Photonics
2023, 5(4): 040101

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Southern University of Science and Technology, College of Engineering, UTS-SUSTech Joint Research Centre for Biomedical Materials and Devices, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen, China
2 City University of Hong Kong, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hong Kong, China
3 Peking University, College of Future Technology, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Beijing, China
4 University of Technology Sydney, Institute for Biomedical Materials and Devices (IBMD), Faculty of Science, Sydney, Australia
In light-sheet fluorescence microscopy, the axial resolution and field of view are mutually constrained. Axially swept light-sheet microscopy (ASLM) can decouple the trade-off, but the confocal detection scheme using a rolling shutter also rejects fluorescence signals from the specimen in the field of interest, which sacrifices the photon efficiency. Here, we report a laterally swept light-sheet microscopy (LSLM) scheme in which the focused beam is first scanned along the axial direction and subsequently laterally swept with the rolling shutter. We show that LSLM can obtain a higher photon efficiency when similar axial resolution and field of view can be achieved. Moreover, based on the principle of image scanning microscopy, applying the pixel reassignment to the LSLM images, hereby named iLSLM, improves the optical sectioning. Both simulation and experimental results demonstrate the higher photon efficiency with similar axial resolution and optical sectioning. Our proposed scheme is suitable for volumetric imaging of specimens that are susceptible to photobleaching or phototoxicity.
light-sheet fluorescence microscopy image scanning microscopy volumetric imaging pixel reassignment Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(1): 016001
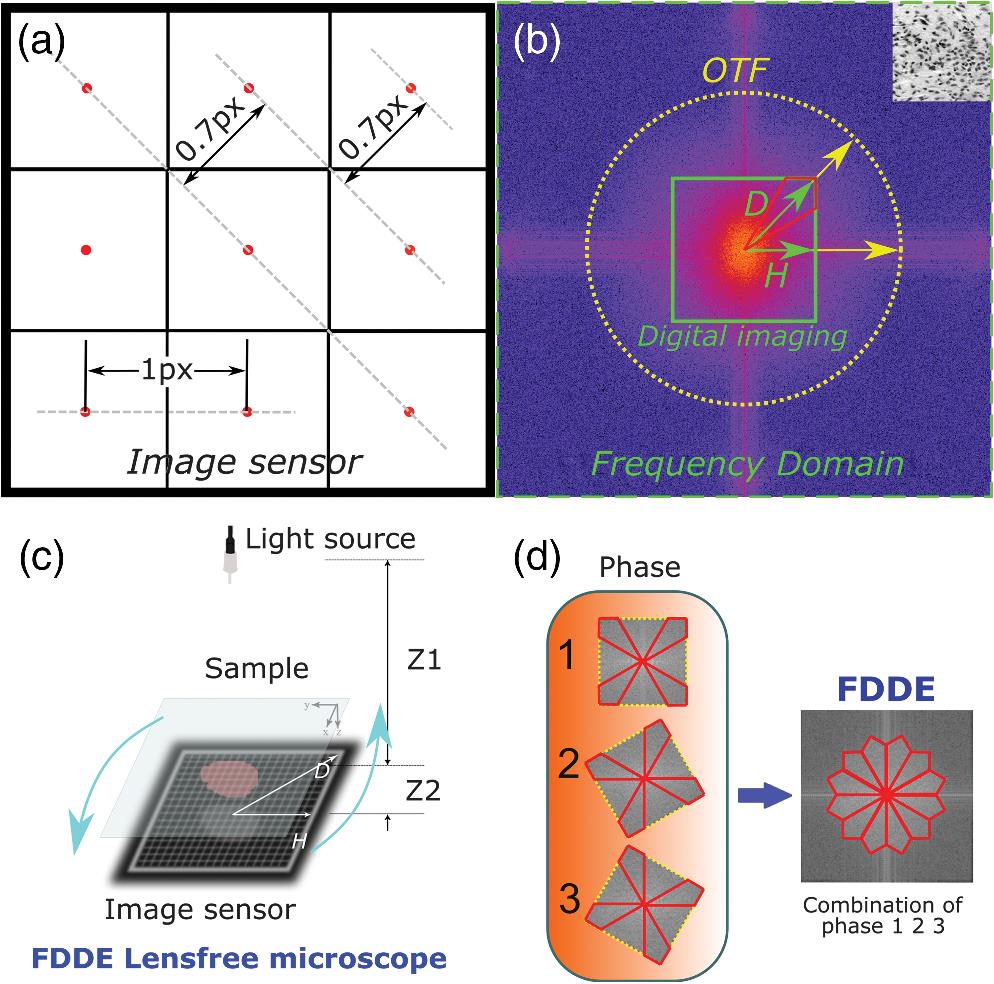
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Peking University, College of Engineering, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Beijing, China
2 Southern University of Science and Technology China, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
3 Beijing Institute of Collaborative Innovation (BICI), Beijing, China
4 Tsinghua University, Department of Automation, Beijing, China
5 University of Technology Sydney, Faculty of Science, Institute for Biomedical Materials & Devices (IBMD), Ultimo, Australia
6 Peking University, School of Physics, Beijing, China
7 Peking University, School of Life Sciences, Biodynamic Optical Imaging Center (BIOPIC), Beijing, China
8 Peking University People’s Hospital Breast Center, Beijing, China
The pixel size of a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera plays a major role in the image resolution, and the square pixels are attributed to the physical anisotropy of the sampling frequency. We synthesize the high sampling frequency directions from multiple frames acquired with different angles to enhance the resolution by 1.4 × over conventional CCD orthogonal sampling. To directly demonstrate the improvement of frequency-domain diagonal extension (FDDE) microscopy, lens-free microscopy is used, as its resolution is dominantly determined by the pixel size. We demonstrate the resolution enhancement with a mouse skin histological specimen and a clinical blood smear sample. Further, FDDE is extended to lens-based photography with an ISO 12233 resolution target. This method paves a new way for enhancing the image resolution for a variety of imaging techniques in which the resolution is primarily limited by the sampling pixel size, for example, microscopy, photography, and spectroscopy.
frequency domain diagonal sampling super-resolution Advanced Photonics
2020, 2(3): 036005
1 北京大学工学院生物医学工程系, 北京100871
2 北京大学人民医院乳腺中心, 北京100044
无透镜显微成像(lens-free microscopy)是一种在不借助透镜的情况下进行成像的技术。它基于Gabor同轴全息原理, 利用面阵探测器采集原始全息图, 随后通过数字图像处理技术重建样本, 从而实现数字显微成像。像素超分辨技术缩小了等效像素, 提供更多细节信息使得再现像的分辨率得以直接提升, 而且多种相位恢复手段通过去除孪生像也达到了间接提高分辨率的目的, 尤其是对密集样本。无透镜显微成像技术突破了传统光学显微镜由透镜带来的空间带宽积的限制, 实现了大视野范围下的高分辨率成像, 因此, 这一技术能够提供大视场下的临床样本快速诊断和准确检测。另外, 新兴的算法和硬件都在不断地加快数据采集和计算速度, 扩展了其在高速运动样本和纳米尺度样本上的应用。最近无透镜技术和其配套硬件设备发展方向趋向于硬件紧凑、算法密集、实时、三维、彩色、高分辨率的便携式分立器件或配件。
无透镜显微术 同轴全息术 相位恢复 像素超分辨 lens-free microscopy in-line holography phase recovery pixel super-resolution
1 北京大学 工学院 生物医学工程系, 北京 100871
2 北京大学 元培学院, 北京 100871
多光子成像技术是一种层析能力好、信噪比高的新型光学成像技术。在皮肤光学三维检测中, 多光子技术已经应用于无创在体成像, 且已得到产业化开发。本文将首先介绍多光子皮肤检测系统的若干核心技术, 即双光子自发荧光技术、二次谐波成像技术、荧光寿命成像技术、相干反斯托克斯-拉曼成像技术等, 然后简要介绍多光子成像系统在皮肤疾病成像检测上的应用, 最后分析该系统的优势和未来可能的发展趋势。
皮肤组织成像 多光子荧光成像 荧光寿命成像 相干反斯托克斯-拉曼 皮肤衰老检测 skin tissue imaging multi-photon fluorescence imaging fluorescence life time imaging coherent anti-stokes raman scattering skin aging detection
1 北京大学 工学院 生物医学工程系, 北京 100871
2 东北大学 中荷生物医学与信息工程学院, 辽宁 沈阳 110167
眼底成像技术可检测临床视网膜组织状态, 其检测结果已成为多种眼底疾病诊断的重要依据。然而, 传统的眼底成像系统需要专业医护人员操作, 且具有体积大、价格昂贵等缺点。随着智能手机的图像采集、存储、数据传输等功能的不断提升, 基于智能手机的眼底成像系统可有效弥补传统眼底成像系统的上述缺陷。在本研究中, 我们设计了照明和成像光路并利用3D打印技术将其小型化, 通过与智能手机相结合实现了对人眼视网膜图像的采集。结果表明, 基于智能手机的眼底相机距离模拟眼的工作距离约为17 mm, 安置于体积仅为88 mm×79 mm×42 mm(长×宽×高)的手机外设配件中。随后, 利用Zemax对系统光学参数进行了进一步优化。经优化后的成像系统, 畸变保持在02%范围内, 场曲小于10 μm。该系统具有便携性良好、无创、价格低廉等优点, 未来可用于多种眼底疾病的社区筛查工作。
眼底成像 便携式设备 成像系统 数值仿真 retinal imaging portable device imaging system numerical simulation
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Engineering Peking University, China
2 School of Optical-Electronic and Computer Engineering Shanghai University of Science and Technology, China
3 Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
4 Bioinfomatics Division, TNLIST MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinformatics and Center for Synthetic & System Biology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
5 Faculty of Science, Institute for Biomedical Materials and Devices (IBMD) University of Technology, Australia
Fluorescence polarization is related to the dipole orientation of chromophores, making fluorescence polarization microscopy possible to reveal structures and functions of tagged cellular organelles and biological macromolecules. Several recent super resolution techniques have been applied to fluorescence polarization microscopy, achieving dipole measurement at nanoscale. In this review, we summarize both diffraction limited and super resolution fluorescence polarization microscopy techniques, as well as their applications in biological imaging.
Fluorescence polarization microscopy super resolution fluorescence anisotropy linear dichroism polarization modulation Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2018, 11(1): 1730002
北京大学工学院生物医学工程系, 北京 100871
随着荧光探针的出现,超分辨成像技术发展迅速,多种不同的超分辨显微技术产生并得到广泛应用。超分辨成像技术的发展为生命科学领域的研究提供了极大便利,也越来越受到研究者的重视。由于传统超分辨显微成像技术在成像速度、观察视野范围、系统成本等方面仍存在一定的限制,新型超分辨显微成像技术的发展让研究人员再次看到超分辨成像领域的曙光。介绍了近年来出现的几种新型超分辨成像技术,包括膨胀样品超分辨技术、表面增强超分辨技术和荧光偏振超分辨技术,旨在总结这些新型超分辨技术的发展,为生命科学领域提供新的技术参考。
成像系统 超分辨显微 膨胀样品超分辨 表面增强超分辨 荧光偏振超分辨 激光与光电子学进展
2018, 55(3): 030006
1 北京大学 元培学院, 北京 100871
2 北京大学 工学院 生物医学工程系, 北京 100871
相比于传统的光学成像技术, 近年来获得快速发展的新型多光子成像技术具有穿透深度大, 组织光损伤小, 信噪比高, 且可方便进行光学层析成像的特点, 故而被广泛应用于包括脑、肿瘤、胚胎在内的多种活体组织成像中。本综述回顾了新型多光子成像技术的诞生与发展历程, 包括微型化双光子成像技术、双光子内窥技术和三光子成像技术, 概括分析了其基本原理与成像特点, 讨论了这一领域具有代表性的最新研究成果, 重点总结了其在生物学基础研究领域和临床医学诊断中的主要应用, 并展望了其未来的应用与发展前景。可以预见, 随着激光器和光探测技术的不断进步, 多光子成像技术将会得到更大的发展与更加广泛的应用。
多光子成像 微型化双光子成像技术 双光子内窥技术 三光子成像技术 multiphoton microscopy miniature two-photon microscopy two-photon endoscopy three-photon microscopy





